EXTRAPLAC - Extension of the Continental Shelf
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (Montego Bay, 1982) lays down a comprehensive regime of law and order in the world’s oceans and seas establishing rules governing all uses of the oceans and their resources and particularly their exploration, exploitation and the regime for deep seabed mining. Part VI of the Convention (Articles 76 to 85) deals with the rights and duties of a coastal State with respect to its continental shelf and resources. Article 76 lays down the rules for the claim and delimitation of the outer limit of the continental shelf by a coastal State.
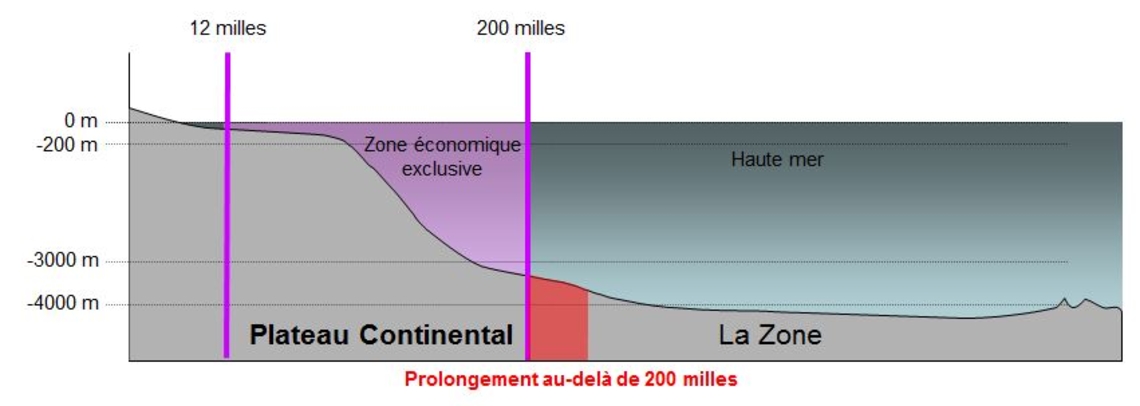
Under this convention, ratified by France in 1996, coastal states have the possibility of extending the maritime areas under their jurisdiction beyond 200 nautical miles, which generally coincide with the limits of the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). These extensions to the high seas can be claimed for the continental shelf (on and below the seafloor), if certain geomorphological and geophysical criteria are met. It is a natural extension of the land at sea.
The claims are examined by a specialized commission of the United Nations, the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf.
EXTRAPLAC is the national program dedicated to French claims. It is led by an inter-ministerial steering committee headed by the Secretary-General for the Sea, and a technical and scientific project group for the collection of data, their exploitation, and the constitution of extension claims for the United Nation’s Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf.
The project group is composed of representatives from MEEM, Ifremer, Shom, IFP-Energies Nouvelles, and Ipev. Ifremer is in charge of the project, which is managed by Geo-Ocean teams.
The maritime domain currently under French jurisdiction occupies an area of nearly 11 million km². France has made claims for 11 areas in three oceans: the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian. This work could lead to the extension of French sovereignty over a maritime domain of more than 1 to 1.5 million km², or 2 to 3 times the size of French metropolitan territory.
What are the challenges of the continental shelf?
The continental shelf is a major issue for France, which has a first-class maritime domain. Is it possible for France to expand?
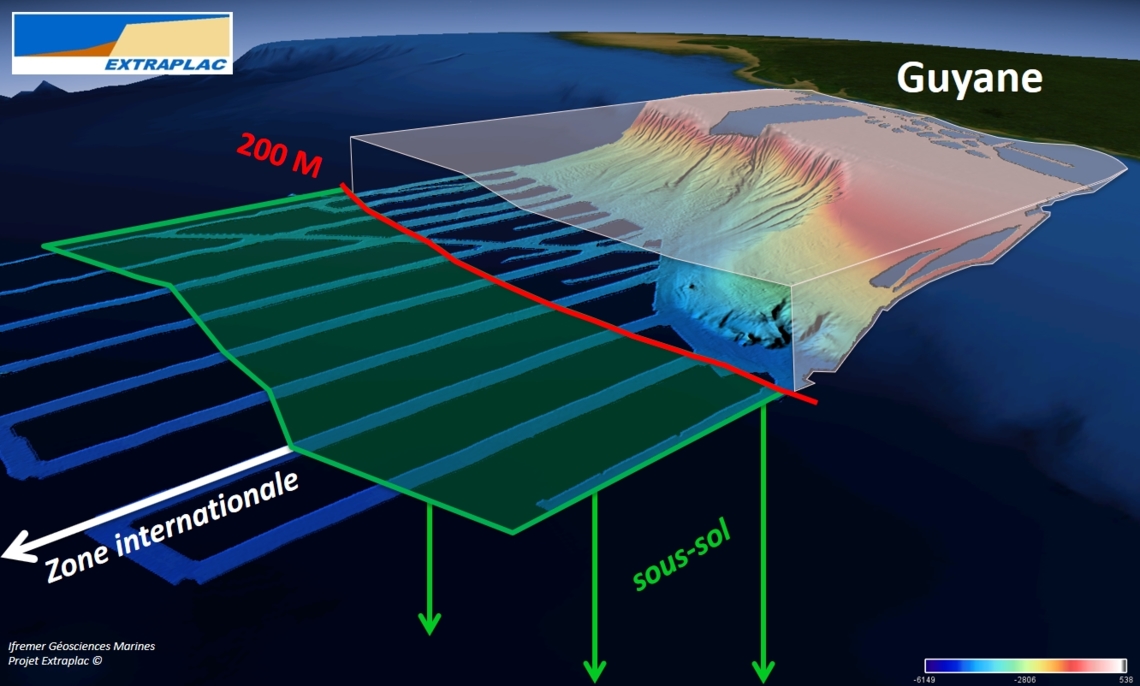
Delimitation of the continental shelf: example of the continental shelf off the coast of French Guiana.